START ON
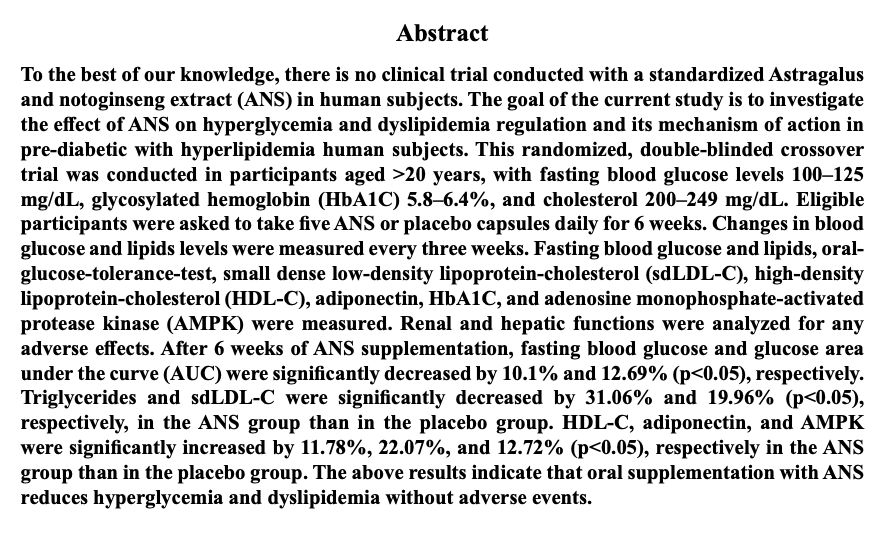
ampk activation
- 18 项体外实验室临床研究
- 2 体内活体临床研究
- 2 项人体临床研究


产品特点
- 空腹血糖 -10.1%
- 甘油三酯 -31.06%
- 低密度胆固醇 sdLDL -19.96%
- 高密度胆固醇 HDL +11.78%
- 脂联素 体内燃脂 +22.07%
- AMPK 魔力蛋白 逆龄代谢 +12.72%
启动新陈代谢:激活 AMPK 代谢开关 魔力蛋白 逆龄代谢
肌肉细胞中的 AMPK上调52%,脂肪细胞中的 AMPK上调300%
科研参考 Scientific journal reference: Adaptive Medicine 5(4): 181-188, 2013 181 DOI: 10.4247/AM.2013.ABD068
糖尿病管理与调节血糖:减少胰岛素抵抗
脂肪细胞中的脂联素上调 103%,胰岛素抵抗脂肪细胞中的脂联素上调 248%
脂联素提升代表着身体在燃烧脂肪。脂联素是一种细胞信使,在肝脏中发挥作用,调节细胞葡萄糖摄取和脂肪燃烧。
科研参考 Scientific journal reference: Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, vol. 4, no. 5, 29 Aug. 2021, pp. 1–8

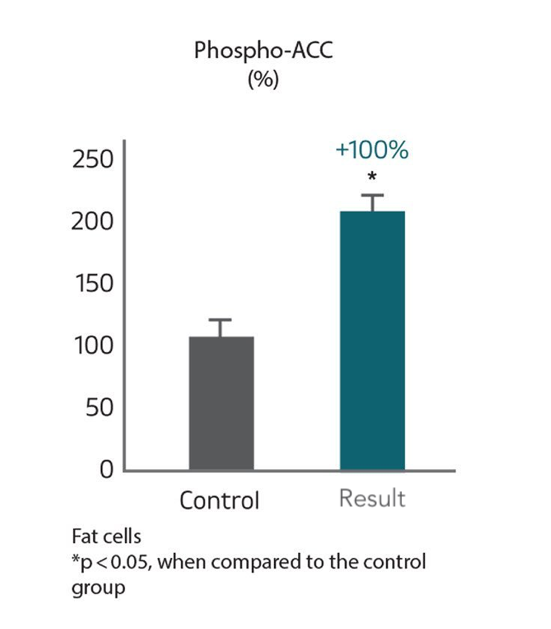
燃烧脂肪 : 提升脂肪细胞内ACC燃脂酶
ACC是脂肪细胞内负责调节脂肪代谢与燃烧的一种生物酶
科研参考 Scientific journal reference: Adaptive Medicine 5(4): 181-188, 2013
我们备有专利配方与及强大的科研团队 临床研究证明产品安全高效
资料参考
- Lin, Hang-Ching, et al. “Method for Enhancing Nutrient Absorption with Astragalosides”; United States Patent and Trademark Office; Patent US8197860B2; June 12, 2012; https://patents.google.com/patent/US8197860B2/en
- Huang, Shih-Chien, et al. “Anti-Hyperglycemic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities of Radix Astragali and Panax Notoginseng Extract in Human Participants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Clinical Trial.” Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, vol. 5, no. 3, 2022; https://www.alliedacademies.org/articles/antihyperglycemic-and-antihyperlipidemic-activities-of-radix-astragali-and-panax-notoginseng-extract-in-human-participants-a-rando-21130.html (full-text PDF)
- Huang, Shih-Chien, et al. “Radix Astragali and Notoginseng Saponins Improve Glucose and Fatty Acid Metabolism through Upregulated Adiponectin and It Downstream Signaling Pathway.” Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, vol. 4, no. 5, 29 Aug. 2021, pp. 1–8; https://www.alliedacademies.org/articles/radix-astragali-and-notoginseng-saponins-improve-glucose-and-fatty-acid-metabolism-through-upregulated-adiponectin-and-it-downstre-18093.html (full-text PDF)
- Zheng, Yijun et al. “A Review of the Pharmacological Action of Astragalus Polysaccharide.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 11 349. 24 Mar. 2020, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00349; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/32265719/
- Wang, Ni et al. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China journal of Chinese materia medica vol. 45,2 (2020): 398-404. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191017.201; https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?doi=10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191017.201
- Stephens, Carissa; “Got Qi? What Chinese Medicine Says about Your Body’s Innate Energy.” Healthline, 25 Feb. 2019; https://www.healthline.com/health/ways-to-balance-qi-for-health#6-tips-for-boosting-qi
- “Astragalus: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning.” Webmd.com, 2019; https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-963/astragalus
- P.Czech1, Michael; “The GLUT4 Glucose Transporter.”; Cell Metabolism; Cell Press; 3 Apr. 2007; https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413107000678
- “Adaptogen Definition – Google Search.”; https://www.google.com/search?q=adaptogen+definition
- Liu, Ping et al. “Anti-Aging Implications of Astragalus Membranaceus (Huangqi): A Well-Known Chinese Tonic.” Aging and disease vol. 8,6 868-886. 1 Dec. 2017, doi:10.14336/AD.2017.0816; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5758356/
- Yang, Yong et al. “Ginseng: An Nonnegligible Natural Remedy for Healthy Aging.” Aging and disease vol. 8,6 708-720. 1 Dec. 2017, doi:10.14336/AD.2017.0707; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5758347/
- Saklayen, Mohammad G. “The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome.” Current Hypertension Reports, vol. 20, no. 2, Feb. 2018, 10.1007/s11906-018-0812-z; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5866840/
- Ormazabal, Valeska, et al. “Association between Insulin Resistance and the Development of Cardiovascular Disease.” Cardiovascular Diabetology, vol. 17, no. 1, 31 Aug. 2018, 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4; https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
- Freeman, Andrew M, and Nicholas Pennings. “Insulin Resistance.” Nih.gov, StatPearls Publishing, 2019; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507839/
- Zheng, Deqiang et al. “Association Between Triglyceride Level and Glycemic Control Among Insulin-Treated Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.” The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism vol. 104,4 (2019): 1211-1220. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01656 https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-lookup/doi/10.1210/jc.2018-01656
- Bertsch, Ruth Ann, and Maqdooda A Merchant. “Study of the Use of Lipid Panels as a Marker of Insulin Resistance to Determine Cardiovascular Risk.” The Permanente journal vol. 19,4 (2015): 4-10. doi:10.7812/TPP/14-237; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4625988/
- Bartlett, Jacquelaine, et al. “Is Isolated Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol a Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factor?” Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, vol. 9, no. 3, May 2016, pp. 206–212, 10.1161/circoutcomes.115.002436; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4871717/
- Wang, T. D., et al. “Efficacy of Cholesterol Levels and Ratios in Predicting Future Coronary Heart Disease in a Chinese Population.” The American Journal of Cardiology, vol. 88, no. 7, 1 Oct. 2001, pp. 737–743, 10.1016/s0002-9149(01)01843-4; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11589839
- Jeppesen, Jørgen, et al. “Low Triglycerides–High High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease.” Archives of Internal Medicine, vol. 161, no. 3, 12 Feb. 2001, p. 361, 10.1001/archinte.161.3.361; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/647239
- Castelli, William P. “Epidemiology of Triglycerides: A View from Framingham.” American Journal of Cardiology, vol. 70, no. 19, 14 Dec. 1992, pp. H3–H9, 10.1016/0002-9149(92)91083-G; https://www.ajconline.org/article/0002-9149(92)91083-G/abstract
- McLaughlin, Tracey, et al. “Use of Metabolic Markers to Identify Overweight Individuals Who Are Insulin Resistant.” Annals of Internal Medicine, vol. 139, no. 10, 18 Nov. 2003, p. 802, 10.7326/0003-4819-139-10-200311180-00007; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14623617/
- Shen, Lan, et al; “Abstract 16300: Initial Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and LDL Paradox in Statin-Naïve Patients Presenting With Acute Coronary Syndrome in China”; Circulation; Volume 138; November 5, 2018; https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/circ.138.suppl_1.16300
- Richter, Erik A, and Neil B Ruderman; “AMPK and the biochemistry of exercise: implications for human health and disease”; The Biochemical journal; vol. 418,2; 2009; 261-75; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2779044/
- Mihaylova, Maria M, and Reuben J Shaw; “The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism”; Nature cell biology; vol. 13,9; 1016-23; 2 Sep. 2011; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249400/
- Buhl, Esben S, et al; “Long-Term AICAR Administration Reduces Metabolic Disturbances and Lowers Blood Pressure in Rats Displaying Features of the Insulin Resistance Syndrome.”; Diabetes; U.S. National Library of Medicine; July 2002; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12086950/
- Entezari, Maliheh et al. “AMPK signaling in diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance and diabetic complications: A pre-clinical and clinical investigation.” Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie vol. 146 (2022): 112563. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112563; https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0753-3322(21)01350-0
- Srikanthan, Krithika et al; “Systematic Review of Metabolic Syndrome Biomarkers: A Panel for Early Detection, Management, and Risk Stratification in the West Virginian Population.”; International journal of medical sciences; vol. 13,1; 25-38; 1 Jan. 2016; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4716817/
- Kadowaki, Takashi, and Toshimasa Yamauchi; “Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors.”; Endocrine Reviews; U.S. National Library of Medicine; May 2005; https://academic.oup.com/edrv/article/26/3/439/2355263
- Khoramipour, Kayvan et al. “Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition.” Nutrients vol. 13,4 1180. 2 Apr. 2021, doi:10.3390/nu13041180; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/33918360/
- Lihn, A S, et a;. “Adiponectin: Action, Regulation and Association to Insulin Sensitivity.;” Obesity Reviews : an Official Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity; U.S. National Library of Medicine; Feb. 2005; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15655035
- Lala, Vasimahmed, and David A Minter. “Liver Function Tests.” Nih.gov, StatPearls Publishing, 2019; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482489/
- Loria, Paola et al. “Liver and diabetes. A vicious circle.” Hepatology research : the official journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology vol. 43,1 (2013): 51-64. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01031.x; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3733501/
- Paschos, P, and K Paletas. “Non alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome.” Hippokratia vol. 13,1 (2009): 9-19; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2633261/
- Stolic, M, et al. “Glucose Uptake and Insulin Action in Human Adipose Tissue—Influence of BMI, Anatomical Depot and Body Fat Distribution.” International Journal of Obesity, vol. 26, no. 1, Jan. 2002, pp. 17–23, 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801850. https://www.nature.com/articles/0801850
- Berg, Jeremy M; “Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase Plays a Key Role in Controlling Fatty Acid Metabolism.”; Biochemistry. 5th Edition; U.S. National Library of Medicine; 1 Jan. 1970; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22381/
- Lally, James S.V., et al. “Inhibition of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase by Phosphorylation or the Inhibitor ND-654 Suppresses Lipogenesis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.” Cell Metabolism, vol. 29, no. 1, Jan. 2019, pp. 174-182.e5, 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.020; https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/pdfExtended/S1550-4131(18)30521-7
- Alam, Fahmida et al. “Metabolic Control of Type 2 Diabetes by Targeting the GLUT4 Glucose Transporter: Intervention Approaches.” Current pharmaceutical design vol. 22,20 (2016): 3034-49. doi:10.2174/1381612822666160307145801 https://www.eurekaselect.com/140253/article
- Pajak, B et al. “2-Deoxy-d-Glucose and Its Analogs: From Diagnostic to Therapeutic Agents.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 21,1 234. 29 Dec. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijms21010234; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6982256/
- Pandey S, Joshi D, Singh S, Ray S, Bhatt AN, Natarajan K, Dwarakanath BS. Dietary Administration of 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Reduces High Fat Diet Induced Obesity and meta-inflammation in Mice. Innov Aging. 2020 Dec 16;4(Suppl 1):920. doi: 10.1093/geroni/igaa057.3379; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7742200/pdf/igaa057.3379.pdf
- Nikolai, Sibylle et al. “Energy restriction and potential energy restriction mimetics.” Nutrition research reviews vol. 28,2 (2015): 100-120. doi:10.1017/S0954422415000062 https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0954422415000062/type/journal_article
- Ralser, M., et al. “A Catabolic Block Does Not Sufficiently Explain How 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Inhibits Cell Growth.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 105, no. 46, 11 Nov. 2008, pp. 17807–17811, 10.1073/pnas.0803090105 https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0803090105
- Abrams, David B., et al. “Area under the Curve (AUC).” Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine, 2013, pp. 125–126; 10.1007/978-1-4419-1005-9_986; https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-1-4419-1005-9_986
- Kim, Ji Hye et al. “Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases.” Journal of ginseng research vol. 41,4 (2017): 435-443. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2016.08.004; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5628327/
- W.L. Chang, et al; “The Inhibitory Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on Glucose and Lipid Production in Human HepG2 Cells.”; Adaptive Medicine; 2013; 5(4); 181-188; https://discover.nulivscience.com/hubfs/InnoSlim/The_Inhibitory_effect_of_Rg1_on_glucose_and_lipid_production_in_human_hepG2_cells.pdf
- Danne, Thomas, et al; “Combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 Inhibitors and Their Role in Diabetes Care.”; Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics; U.S. National Library of Medicine; June 2018; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29916741
- Chang, Tsu-Chung, et al. “Effect of Ginsenosides on Glucose Uptake in Human Caco-2 Cells Is Mediated through Altered Na+/Glucose Cotransporter 1 Expression.” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, vol. 55, no. 5, Mar. 2007, pp. 1993–1998, 10.1021/jf062714k; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17269785/
- Ziello, Jennifer E et al; “Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia.”; The Yale journal of biology and medicine; vol. 80,2; 2007; 51-60; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2140184/
- C.W. Wang, et al; ” An Essential Role of cAMP Response Element Binding Protein in Ginsenoside Rg1-Mediated Inhibition of Na1/ Glucose Cotransporter 1 Gene Expression.”; Mol Pharmacol; 2015; 88(6); 1072-83; http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=26429938
- He, Qing et al. “Regulation of HIF-1{alpha} activity in adipose tissue by obesity-associated factors: adipogenesis, insulin, and hypoxia.” American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism vol. 300,5 (2011): E877-85. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00626.2010; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3093977/
- Zhang, Silin et al. “Ginsenoside Compound K Regulates HIF-1α-Mediated Glycolysis Through Bclaf1 to Inhibit the Proliferation of Human Liver Cancer Cells.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 11 583334. 8 Dec. 2020, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.583334; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7753211/
- Gwozdziewiczová, Simona, et al; “TNF-Alpha in the Development of Insulin Resistance and Other Disorders in Metabolic Syndrome.”; Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia; U.S. National Library of Medicine; June 2005; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16170397
- Lee, Davy C W, and Allan S Y Lau. “Effects of Panax ginseng on tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated inflammation: a mini-review.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 16,4 2802-16. 30 Mar. 2011, doi:10.3390/molecules16042802; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6260618/
- Cesari, Matteo et al; “Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): a key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions.”; Cardiovascular therapeutics; vol. 28,5; 2010; e72-91; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2958211/
- Sam, Susan et al; “Relation of abdominal fat depots to systemic markers of inflammation in type 2 diabetes.”; Diabetes care; vol. 32,5; 2009; 932-7; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2671130/
- Zhang, Hong-Sheng, and Sheng-Qi Wang. “Notoginsenoside R1 from Panax Notoginseng Inhibits TNF-α-Induced PAI-1 Production in Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells.” Vascular Pharmacology, vol. 44, no. 4, Apr. 2006, pp. 224–230, 10.1016/j.vph.2005.12.002; https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1537189105002600
- Y.C. Huang, et al; “Effect and Mechanism of Ginsenosides CK and Rg1 on Stimulation of Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.”; J. Agric. Food Chem; 2010; 58; 6039–6047; https://nulivscience.com/application/files/9815/5500/9393/1._Effect_and_mechanism_of_ginsebosides_CK_and_Rg1_on_stimulation_of_glucose_uptake_in_3T3-L1_adipocytes.pdf